

Planning and Development
Michael McElroy
Planning and Development Homepage
Director of Planning and Development
Michael McElroy
Contact Information
Office of Public Works
800 E Overland, Suite 200
El Paso, Texas 79901
Phone: (915) 273-3330
Monday-Friday
8:00 am - 5:00 pm
Useful Links
Road Cut Permit
Driveway Permit
Property Donations
Reporting a Street Light Out EPE
GIS Enterprise
Go-Post
FAQs
View Frequently Asked Questions
Links to Municipalities
City of El Paso
City of Socorro
City of Horizon
City of San Elizario
Town of Anthony
Town of Clint
Village of Vinton
Links to Agencies
LID TOOLBOX
The following LID strategies can be adapted to suit the unique environmental conditions of the Chihuahua Desert. Each tool focuses on managing stormwater naturally while supporting the desert ecosystem.








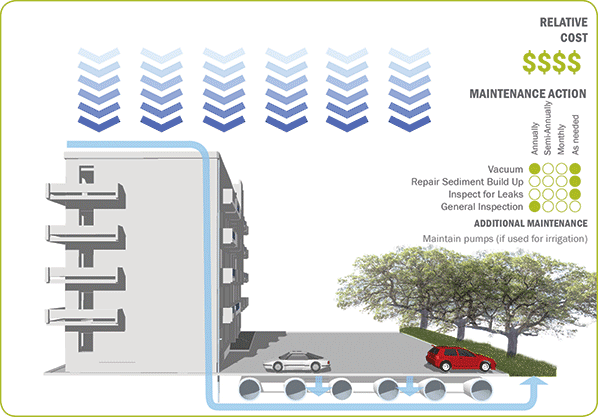


Maintenance Checklist [PDF]
Inspection & Maintenance Schedule: Green Roofs [PDF]